What Are the Main Functions of the Hypothalamus? Understanding the Brain’s Control CenterThe human brain is a complex organ, and within it lies a small but powerful region called the hypothalamus. Though it is only about the size of an almond, the hypothalamus is responsible for managing many critical functions that keep the body in balance. From regulating temperature to controlling hunger, this part of the brain works silently behind the scenes to maintain stability in the body.
In this topic, we’ll explore the main functions of the hypothalamus, why they matter, and how this tiny structure plays a central role in your daily life.
What Is the Hypothalamus?
The hypothalamus is located at the base of the brain, just below the thalamus and above the brainstem. It is a vital part of the diencephalon, connecting the nervous system to the endocrine system through its interaction with the pituitary gland.
Even though it’s small, the hypothalamus is one of the most important regulators of internal body processes.
Why Is the Hypothalamus Important?
The hypothalamus acts as the body’s internal thermostat and control center. It detects changes in the body and responds by releasing hormones or triggering responses to restore balance. Its main job is to maintain homeostasis, which means keeping the body’s internal environment stable and consistent.
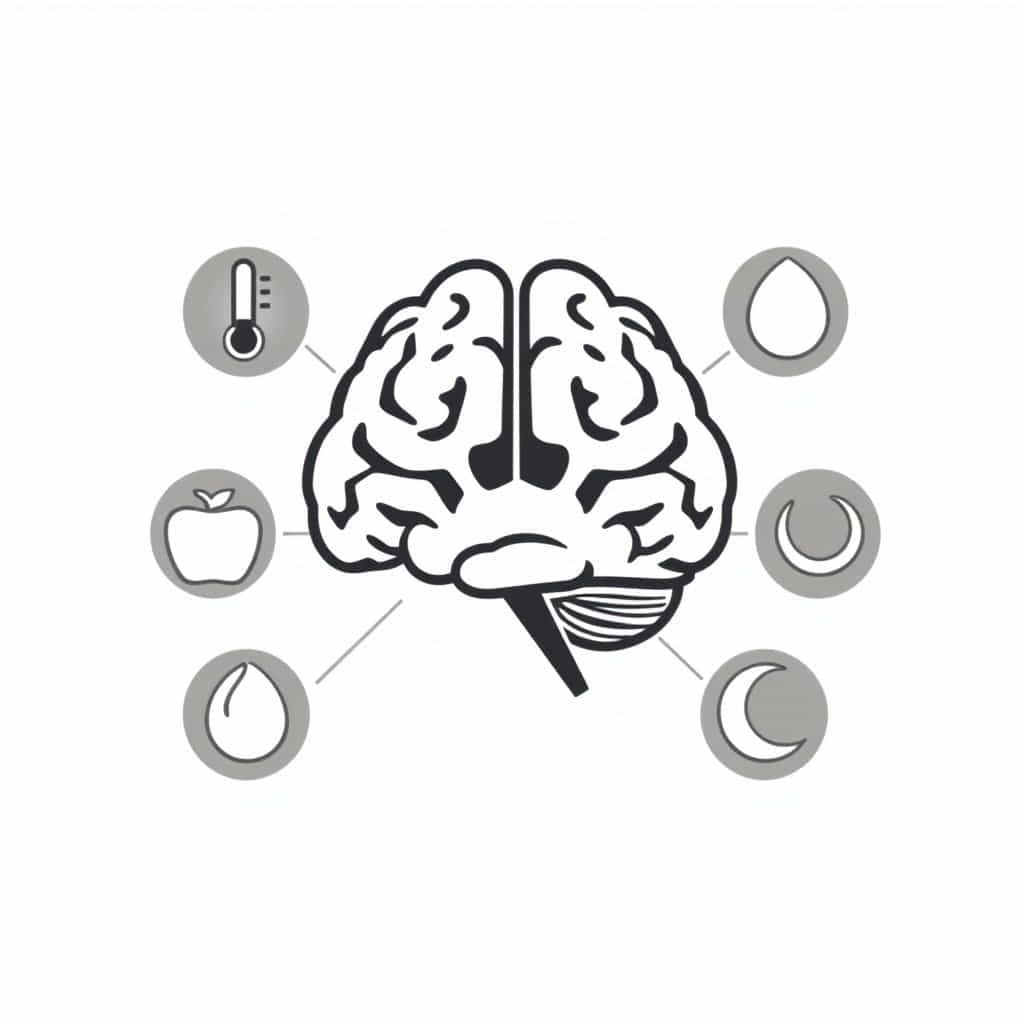
Key Functions of the Hypothalamus
Let’s break down the major roles of the hypothalamus one by one. These are the main functions you should be aware of
1. Regulation of Body Temperature
One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is controlling body temperature. It senses internal temperature changes and activates mechanisms to cool or warm the body. For example
-
Sweating when you’re too hot
-
Shivering when you’re too cold
This automatic response helps protect the body from damage due to extreme temperatures.
2. Control of Hunger and Satiety
The hypothalamus contains centers that regulate hunger and fullness. When energy levels drop, it triggers sensations of hunger. After eating, it sends signals to stop eating. It balances energy intake to support metabolism and body weight.
This is why damage to the hypothalamus can result in weight gain, weight loss, or abnormal eating behaviors.
3. Thirst Regulation
Along with hunger, the hypothalamus monitors fluid levels in the body. When you’re dehydrated, it stimulates thirst to encourage you to drink water. This is essential for keeping the electrolyte balance and blood pressure in check.
4. Sleep-Wake Cycle Control
The hypothalamus helps regulate the circadian rhythm, which is your internal clock. This rhythm influences your sleep patterns, alertness, and hormone release throughout the day.
It plays a role in both falling asleep and waking up by interacting with other parts of the brain that manage light perception and hormonal cycles.
5. Regulation of Emotions and Behavior
Although emotions are largely controlled by the limbic system, the hypothalamus has a close connection to emotional responses. It helps regulate anger, pleasure, fear, and even sexual behavior.
It does this by influencing the release of hormones and responding to signals from other parts of the brain that handle emotional processing.
6. Endocrine System Control via the Pituitary Gland
The hypothalamus directly influences the pituitary gland, sometimes referred to as the master gland. It produces releasing and inhibiting hormones that tell the pituitary when to release its own hormones.
These hormones regulate functions like
-
Growth
-
Reproduction
-
Stress response
-
Thyroid activity
This connection means the hypothalamus is a bridge between the brain and the hormonal system.
7. Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Regulation
The hypothalamus plays a supporting role in managing blood pressure and heart rate by controlling parts of the autonomic nervous system. When the body faces stress or needs to adjust to activity levels, the hypothalamus helps coordinate changes in heart function.
8. Body Energy Balance and Metabolism
By managing hunger, satiety, and hormone levels, the hypothalamus helps control how the body uses and stores energy. It contributes to metabolic rate, ensuring that you use energy efficiently based on your needs.
9. Sexual Behavior and Reproductive Functions
The hypothalamus also contributes to sexual development and behavior. It releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which prompts the pituitary to produce sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone.
These hormones affect fertility, libido, and reproductive health in both males and females.
Summary of Hypothalamus Functions
To summarize, check all that are a function of the hypothalamus
-
Regulating body temperature
-
Controlling hunger and fullness
-
Managing thirst
-
Regulating sleep-wake cycles
-
Influencing emotional behavior
-
Controlling the endocrine system via the pituitary gland
-
Managing heart rate and blood pressure
-
Balancing energy and metabolism
-
Regulating sexual behavior and reproduction
All these functions work together to keep the body in balance and ready to adapt to changing conditions.
The hypothalamus might be small, but it has a big job. From keeping your body temperature just right to telling you when to eat or sleep, this brain region is essential for everyday life. It coordinates physical, emotional, and hormonal responses to keep you feeling stable and healthy.
Understanding how the hypothalamus works helps us appreciate how the brain and body stay connected. Whether you’re learning about biology or curious about how your body functions, knowing the key roles of the hypothalamus gives insight into one of the most important systems that keeps us alive and well.