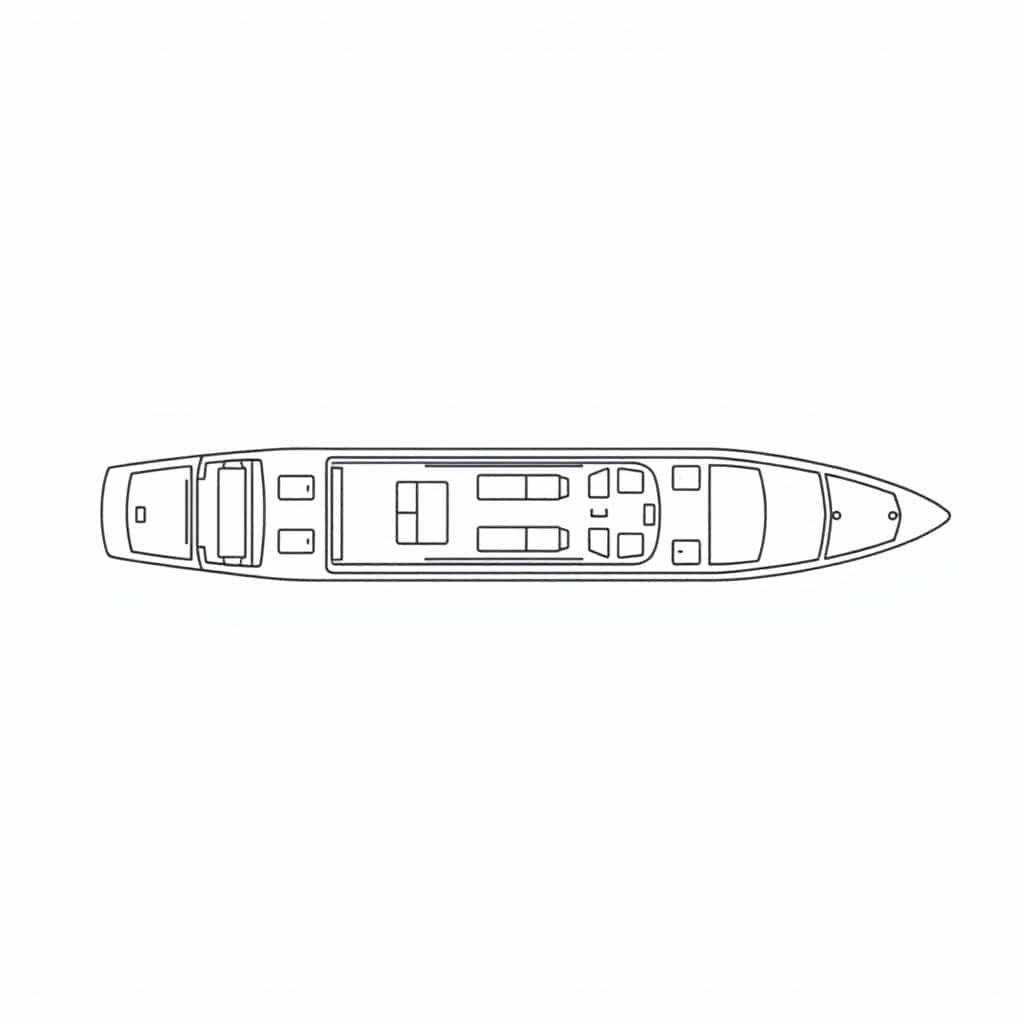
General Arrangement Plan of Ship A Comprehensive GuideA General Arrangement Plan (GAP) is one of the most crucial documents in ship design and construction. This plan provides a detailed representation of how a ship’s internal and external spaces are organized and helps ensure that the vessel operates efficiently, safely, and comfortably. The General Arrangement Plan of a ship is essentially the blueprint that outlines the positioning of various compartments, machinery, and crew areas within the ship.
In this topic, we will explore the importance of the General Arrangement Plan, its components, and how it plays a vital role in both the design and operation of a ship.
What is a General Arrangement Plan?
The General Arrangement Plan of a ship is a schematic representation that depicts the layout of the ship’s internal and external elements. It includes the arrangement of decks, cabins, bulkheads, cargo holds, machinery spaces, and other essential features. The plan provides a clear understanding of the flow of passengers, crew, and cargo within the vessel, which is crucial for safety, efficiency, and functionality.
In essence, the GAP is a detailed diagram that enables designers, engineers, and operators to visualize how all the parts of the ship interact with one another. It helps in ensuring compliance with maritime safety regulations and also assists in identifying potential areas for improvement in the ship’s design.
Importance of a General Arrangement Plan
The General Arrangement Plan serves several purposes, making it a vital document throughout the lifecycle of a ship. Here are some of its key roles
-
Design Efficiency The GAP ensures that the ship is designed with efficient use of space. It helps designers optimize the placement of machinery, living spaces, and cargo areas, ensuring that the vessel can operate effectively without overcrowding or wastage of space.
-
Safety Compliance One of the main objectives of the General Arrangement Plan is to ensure the ship complies with international maritime safety regulations. It takes into account safety measures such as escape routes, fire safety systems, and lifeboat placements, ensuring that the ship meets the necessary standards.
-
Operational Planning The General Arrangement Plan also helps operators plan the day-to-day activities on board the ship. By understanding the layout, they can plan the most efficient routes for crew and passengers, streamline loading and unloading processes, and ensure that everything is in place for smooth operations.
-
Regulatory Approval Before a ship can be built or put into service, its General Arrangement Plan must typically be submitted to regulatory bodies like the International Maritime Organization (IMO) or local maritime authorities for approval. This is to ensure that the design complies with various international standards for safety, environmental protection, and operational efficiency.
Key Components of a General Arrangement Plan
A General Arrangement Plan is a comprehensive document that includes a variety of elements. Each component plays a vital role in the ship’s design and functionality. Let’s take a look at some of the most common components featured in the plan
1. Deck Layout
The deck layout outlines the different levels of the ship, including the main deck, lower deck, and any additional decks. It includes the locations of all essential spaces, such as cargo holds, engine rooms, and passenger cabins. Each deck is numbered or labeled, making it easy to identify the different levels within the ship.
2. Compartmentalization
Ship compartments are sections of the vessel that are separated by bulkheads. The GAP shows how these compartments are organized and connected. Compartmentalization is essential for safety, as it helps in limiting the spread of fire or flooding in case of an emergency. This section of the plan typically highlights the ship’s watertight doors and fireproof walls.
3. Machinery Spaces
Machinery spaces include areas such as the engine room, boiler room, and control rooms, where essential equipment for the ship’s operation is located. These spaces are critical to the functioning of the ship, and the General Arrangement Plan clearly marks the location of various machinery and systems within these areas.
4. Cargo Holds and Storage Areas
For cargo ships, the cargo holds are a vital part of the General Arrangement Plan. This section of the plan outlines the various cargo compartments, specifying the capacity and layout for different types of cargo. For passenger ships, this section might focus on the placement of amenities such as dining areas, lounges, and recreational spaces.
5. Passenger and Crew Areas
Passenger ships often have dedicated spaces for passengers, crew members, and officers. The GAP outlines the arrangement of these areas, including cabins, dining rooms, recreation rooms, and crew lounges. For safety, it also indicates the locations of life-saving equipment such as lifeboats and life rafts.
6. Escape Routes and Safety Features
One of the most critical aspects of the General Arrangement Plan is the identification of escape routes and safety features. This includes the positioning of emergency exits, fire escapes, lifeboats, and life rafts. These elements are designed to help people evacuate the ship quickly in the event of an emergency.
How the General Arrangement Plan is Used in Shipbuilding
During the design and construction phases, the General Arrangement Plan serves as the primary reference for shipbuilders and engineers. Here’s how it’s used
-
Initial Design The General Arrangement Plan is created during the conceptual and detailed design stages. It helps designers visualize the ship’s layout and ensure that all components are placed efficiently.
-
Construction During construction, the General Arrangement Plan is used as a reference guide for workers to ensure that the ship is built according to specifications. It provides details on the size and placement of various components, making it easier for construction teams to assemble the ship.
-
Testing and Sea Trials Once the ship is constructed, it undergoes testing and sea trials. The General Arrangement Plan is used to monitor the vessel’s performance and ensure that all systems are functioning correctly.
-
Operational Use After construction, the General Arrangement Plan is used for day-to-day operations, maintenance, and repairs. It allows crew members to quickly locate equipment, machinery, and emergency exits when needed.
The General Arrangement Plan of a ship is an essential tool in ship design, construction, and operation. By providing a detailed layout of the ship’s internal and external components, it ensures that the vessel is efficient, safe, and compliant with international regulations. Whether for passenger ships, cargo vessels, or military ships, the General Arrangement Plan plays a pivotal role in ensuring smooth operations at sea.
Understanding the significance of this plan can help you appreciate the complexities involved in shipbuilding and maritime operations. From ensuring safety to enhancing operational efficiency, the General Arrangement Plan remains one of the most important documents in the maritime industry.